 by our College Data Analytics Team
by our College Data Analytics TeamDo you ever wonder why you have green eyes and your sister has blue eyes? In the study of Genetics you will follow in the footsteps of that famous monk, Gregor Mendel, who discovered how physical traits were passed through observing generations of peas. He pioneered the research in genetics, how DNA works, and the four letter codes that DNA is made up of.
During your time as a Genetics major you will learn all aspects of cell growth, reproduction, and mutations. Mutations are responsible for cancer as well as a host of other diseases. You will also explore Darwin's theory of natural selection.
Some of the courses you will take are: biochemistry, populations genetics, developmental genetics, molecular genetics, evolutionary genetics, genetic data analysis, human genetics, chemistry, advanced mathematics, biology, organic chemistry.
Concentrations in this major include: Molecular Genetics; Microbial and Eukaryotic Genetics; Animal Genetics; Plant Genetics; Human and Medical Genetics; and Genome Sciences. This major is most often offered as a Master's or Ph.D. However, some schools offer it as a Bachelor's degree.
Genetics was the 206th most popular major in the 2021-2022 school year. Colleges in the United States reported awarding 1,698 degrees in this year alone. This year's Best Genetics Schools ranking compares 36 of them to identify the best overall programs in the country. Explore this or one of our many other custom genetics rankings further below.
The study of genetics can be quite fascinating, but it also can take a lot of work and dedication. A passion for science and discovery will help you get through long hours studying math and science and memorizing formulas. You will also be studying evolution and history. Curiosity, innovation and ability to adapt to new technology will aid you. Do not get frustrated; persistence is the key to success in this major.
You will be working closely with peers and professors for a variety of group projects. Interpersonal and teamwork skills will aid you in completing these projects. Communication skills will help you write clearly when reporting your discoveries in lab, as well as complete research papers. Time management and organization will help you balance time spent in the lab with your other assignments.
New students will need to have completed high school or a GED program and each school will have their own minimum GPA and SAT/ACT test requirements. In addition to these basic genetics program qualifications, to serve in some genetics careers, special certification may be required outside of your degree.
Genetics degree levels vary. You can get anything from a in genetics to the highest genetics degree, a . Genetics programs can take anywhere between one to four or more years for a full-time student to complete.
| Degree | Credit Requirements | Typical Program Length |
|---|---|---|
| Associate Degree | 60-70 credits | 2 years |
| Bachelor’s Degree | 120 credits | 4 years |
| Master’s Degree | 50-70 credits | 1-3 years |
| Doctorate | Program required coursework including thesis or dissertation | At least 4 years |
A doctor's degree is the most common level of education achieved by those in careers related to genetics, with approximately 25.9% of workers getting one. People currently working in careers related to genetics tend obtained the following education levels.
| Level of Education | Percentage of Workers |
|---|---|
| Post-Doctoral Training | 31.5% |
| Doctoral Degree | 26.4% |
| Bachelor’s Degree | 22.1% |
| Master’s Degree | 13.5% |
| Associate’s Degree (or other 2-year degree) | 2.0% |
About 56.7% of workers in careers related to genetics obtain at least doctor's degrees. View the chart below to get an idea of what degree level most of those in genetics careers have.
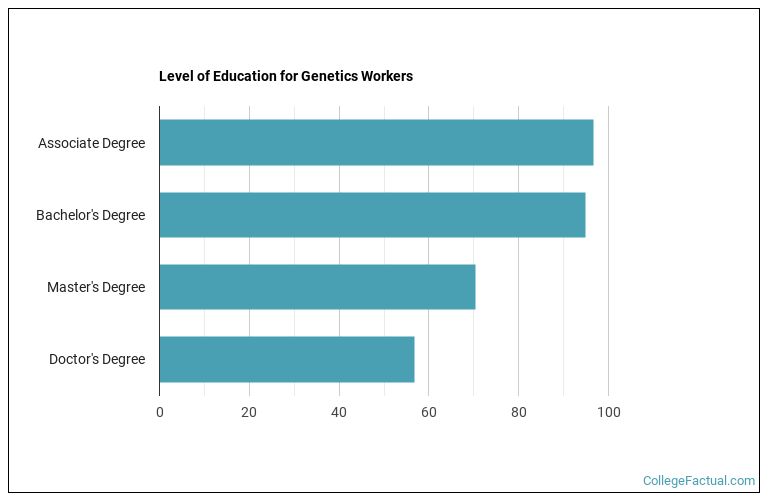
This of course varies depending on which genetics career you choose.
Most people interested in this field will continue their education to get a minimum of a master's degree. You may also decide to focus on medicine, veterinary medicine, or biology in graduate school.
If you do not want to continue your education, genetics majors can also find work upon graduating in a number of fields. Some options include government or independent research, agricultural laboratories, botanical gardens, national parks or private research.
Want a job when you graduate with your genetics degree? Genetics careers are expected to grow 12.3% between 2016 and 2026.
The following options are some of the most in-demand careers related to genetics.
| Occupation Name | Projected Jobs | Expected Growth |
|---|---|---|
| Medical Scientists | 136,100 | 13.4% |
| Biological Science Professors | 71,700 | 15.1% |
| Natural Sciences Managers | 62,300 | 9.9% |
| Biological Scientists | 41,800 | 8.0% |
Recently graduated genetics students earned an average of $35,631 in <nil>. Earnings can range from as low as $19,112 to as high as $89,484. As you might expect, salaries for genetics graduates vary depending on the level of education that was acquired.
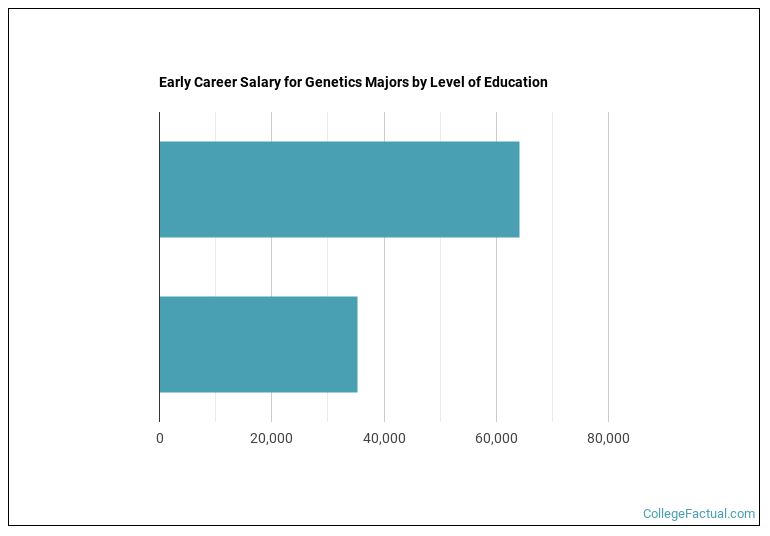
Salaries for genetics graduates can vary widely by the occupation you choose as well. The following table shows the top highest paying careers genetics grads often go into.
| Occupation Name | Median Average Salary |
|---|---|
| Natural Sciences Managers | $139,680 |
| Biological Science Professors | $97,340 |
| Medical Scientists | $96,420 |
| Biological Scientists | $83,600 |
With over 231 different genetics degree programs to choose from, finding the best fit for you can be a challenge. Fortunately you have come to the right place. We have analyzed all of these schools to come up with hundreds of unbiased genetics school rankings to help you with this.
Genetics is one of 14 different types of Biological & Biomedical Sciences programs to choose from.
| Major | Annual Graduates |
|---|---|
| General Genetics | 735 |
| Human/Medical Genetics | 355 |
| Molecular Genetics | 284 |
| Genome Sciences/Genomics | 198 |
| Animal Genetics | 69 |
| Related Major | Annual Graduates |
|---|---|
| General Biology | 106,032 |
| Biochemistry, Biophysics & Molecular Biology | 14,558 |
| Neurobiology & Neurosciences | 12,616 |
| Physiology & Pathology Sciences | 9,568 |
| Ecology, Evolution & Systematics Biology | 7,935 |